Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is commonly known as BPH. BPH is a common condition that affects men as they age, and can cause a range of symptoms that can affect their quality of life. In this article, we will be discussing the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for BPH.
What is BPH?
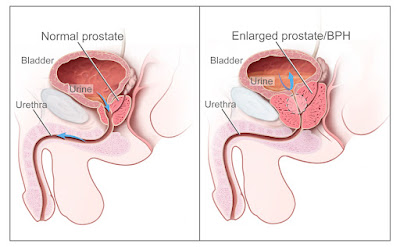
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. As the prostate gland grows, it can squeeze the urethra, causing a range of urinary symptoms.
Causes of BPH:
The exact cause of BPH is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur as men age. As men age, their levels of testosterone decrease, and their levels of estrogen increase, which can cause the prostate gland to grow.
Symptoms of BPH:
The symptoms of BPH can vary from mild to severe and can include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine flow
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Urgency to urinate
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
Diagnosis of BPH:
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of BPH, it's important to see a doctor. The doctor will perform a physical exam, including a digital rectal exam, and may also order other tests, such as a urine flow test or a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, to rule out other conditions.
Treatment options for BPH:
The treatment options for BPH depend on the severity of your symptoms. For mild symptoms, your doctor may recommend watchful waiting and making lifestyle changes, such as limiting fluids before bedtime and avoiding caffeine and alcohol. For more severe symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medications, such as alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, to help relax the muscles in the prostate gland and reduce its size. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part of the prostate gland.
Conclusion:
So there you have it, our overview of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Remember, if you are experiencing any symptoms of BPH, it's important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right treatment, you can manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.